VSCode for Haskell Development
Haskell is a purely functional programming language. The VSCode extension Haskell for Visual Studio Code has been configured to develop Haskell code in the Docker container remotely. This blog explains how to use the VSCode editor to develop Haskell programs. The features, where you can find the table, summarises the features that HLS supports. Many of these are standard LSP features.
Install using docker
Create the following Dockerfile1:
FROM ubuntu:20.04
ARG USERNAME=ojitha
ARG USER_UID=1000
ARG USER_GID=$USER_UID
# Create the user
RUN groupadd --gid $USER_GID $USERNAME \
&& useradd --uid $USER_UID --gid $USER_GID -m $USERNAME \
&& apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y sudo \
&& echo $USERNAME ALL=\(root\) NOPASSWD:ALL > /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME \
&& chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME \
&& apt-get install build-essential curl libffi-dev libffi7 libgmp-dev libgmp10 libncurses-dev libncurses5 libtinfo5 -y
# This is necessary to attach VSCode later
USER $USERNAME
WORKDIR /home/$USERNAME
To create image
docker build -t ojhaskell .
After the image created, create the docker instance as follows:
docker run -it ojhaskell
You will get the bash shell to install the GhCup2. Execute the following command.
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://get-ghcup.haskell.org | sh
In the installation process, you will get the following questions to answer; you can accept the default by pressing the enter key. However, HLS default is N, which should be Y because we need to HLS to run the Haskell extension in the VSCode.

Installation may take time. At the end you may get the following message if everything is successful:

If the message is different, you have to add the contents of the /home/$USERNAME/.ghcup/env to the .bashrc file. When you type ghci, it should give you a Haskell prompt.
For example:
# add by ojitha
case ":$PATH:" in
*:"/home/ojitha/.ghcup/bin":*)
;;
*)
export PATH="/home/ojitha/.ghcup/bin:$PATH"
;;
esac
case ":$PATH:" in
*:"$HOME/.cabal/bin":*)
;;
*)
export PATH="$HOME/.cabal/bin:$PATH"
;;
esac
To verify all the components are install run
ghcup tui
which will give you

At least above components should be installed.
VSCode development
Install the VSCode docker extension. In the docker

As shown above, you can right-click ojhaskell and attach VSCode. That will open a new instance of the VSCode.
Most of cases, Ubuntu use dash shell instead of bash shell.
In Ubuntu, bin/sh is a dash shell. Run the following command to verify your shell
ls -l `which sh`
# lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 4 Jul 18 2019 /usr/bin/sh -> dash
If dash, run the sudo dpkg-reconfigure dash to change this to bash shell as follows.

Close the current VSCode and reattach VSCode again. You are ready to install the VSCode Haskell extension3.
Complete Docker image for Haskell
All the above manual operation can be included in the Dockerfile as follows:
FROM ubuntu:20.04
ARG USERNAME=ojitha
ARG USER_UID=1000
ARG USER_GID=$USER_UID
# Create the user
RUN groupadd --gid $USER_GID $USERNAME \
&& useradd --uid $USER_UID --gid $USER_GID -m $USERNAME \
&& apt-get update \
&& apt-get install -y sudo \
&& echo $USERNAME ALL=\(root\) NOPASSWD:ALL > /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME \
&& chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/$USERNAME
RUN apt-get install build-essential curl vim libffi-dev libffi7 libgmp-dev libgmp10 libncurses-dev libncurses5 libtinfo5 -y
USER $USERNAME
WORKDIR /home/$USERNAME
# # ==================================
# * any nonzero value for noninteractive installation
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_NONINTERACTIVE=1
# * any nonzero value to not trigger the upgrade
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_NO_UPGRADE=0
# * any nonzero value for more verbose installation
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_VERBOSE=0
# * the ghc version to install
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_GHC_VERSION=9.2.7
# * the cabal version to install
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_CABAL_VERSION=3.6.2.0
# * whether to install latest hls
ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_INSTALL_HLS=Y
# # ==================================
# * any nonzero value to only install ghcup
# ENV BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_MINIMAL=0
# * any nonzero value to respect The XDG Base Directory Specification
# ENV GHCUP_USE_XDG_DIRS=1
# * BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_INSTALL_NO_STACK - disable installation of stack
# * BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_INSTALL_NO_STACK_HOOK - disable installation stack ghcup hook
# * BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_ADJUST_BASHRC - whether to adjust PATH in bashrc (prepend)
# * BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_ADJUST_CABAL_CONFIG - whether to adjust mingw paths in cabal.config on windows
# * BOOTSTRAP_HASKELL_DOWNLOADER - which downloader to use (default: curl)
# * GHCUP_BASE_URL - the base url for ghcup binary download (use this to overwrite https://downloads.haskell.org/~ghcup with a mirror)
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://get-ghcup.haskell.org | sh"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo '# add by $USER' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo 'case \":$PATH:\" in' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' *:\"$HOME/.ghcup/bin\":*)' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' ;;' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' *)' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' export PATH=\"$HOME/.ghcup/bin:$PATH\"' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' ;;' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo 'esac' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo 'case \":$PATH:\" in' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' *:\"$HOME/.cabal/bin\":*)' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' ;;' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' *)' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' export PATH=\"$HOME/.cabal/bin:$PATH\"' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo ' ;;' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo 'esac ' >> ~/.bashrc"]
RUN ["/bin/bash", "-c", "echo '' >> ~/.bashrc"]
# set bash to default
RUN echo "dash dash/sh boolean false" | sudo debconf-set-selections
RUN sudo dpkg-reconfigure -f noninteractive dash
This will simplify your process of creating the Haskell development environment. I set the minimum environment variables4 create the same above image.
To create the image from the above Dockerfile:
docker build --no-cache -t testhaskell .
When after image has been created run the following command to create a container:
docker run -it --rm -v "./work":/home/ojitha/work testhaskell
You can attach VSCode to this instance without any further configurations.
Features
Some of the features are:
- Shows ingoing and outgoing calls for a function.

Call hierarchy - Apply Hlint fixes

Apply Hlint fixes - Qualify imported names
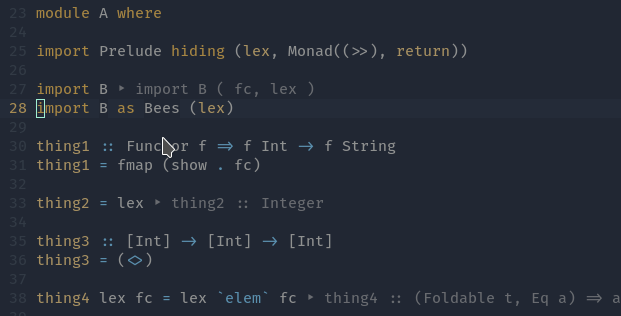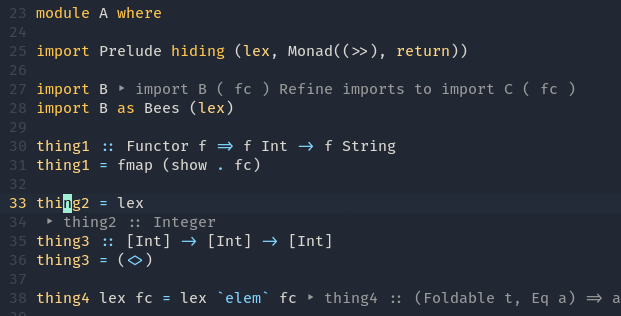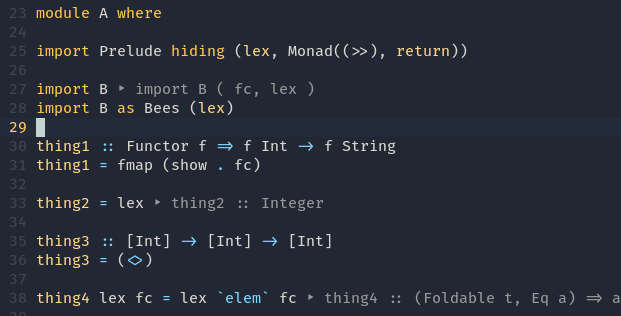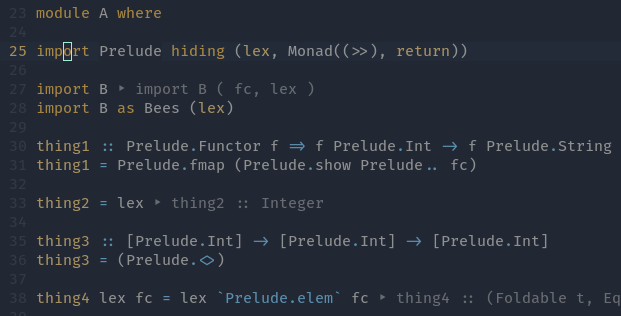
Qualify imported names - Fold definition

Fold definition
References:


Comments
Post a Comment
commented your blog